-
-
Building 5,18 Yueluo Road, Yuepu Town, Baoshan District, Shanghai, China
Call Anytime
+86 131 2053 3622Overview of Di-tert-butyl Dicarbonate Products
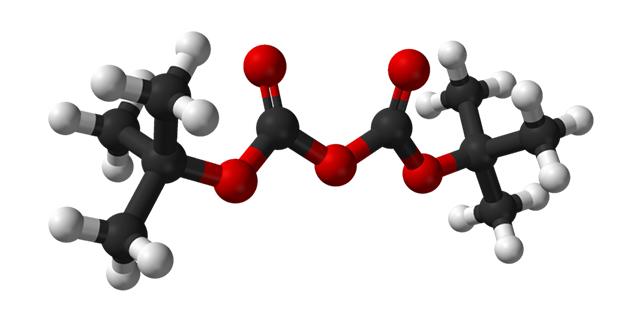
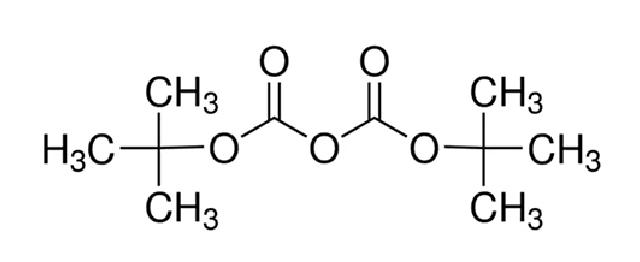
Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate (Diboc) is a novel amino protective agent utilized for introducing tert-butoxycarbonyl (BOC) protection in organic synthesis. It is particularly suitable for the amino protection of amino acids and finds extensive application in medicine, protein and peptide synthesis, biochemistry, food, cosmetics, and other product syntheses. The product appears as a colorless crystal or liquid with a melting point of 22–23°C, a boiling point of 56–57°C/66Pa, a refractive index (ND20) of 1.409, and a relative density (d4) of 0.950. It is soluble in tetrahydrofuran, n-hexane, benzene, trichloromethane, and other organic solvents but only slightly soluble in water.

Proteins serve as the primary carriers of biological functions, while amino acids constitute their fundamental building blocks. The intrinsic properties of amino acids underpin the structural and functional diversity of proteins. Besides providing raw materials for protein synthesis, free amino acids in the body participate in various biological functions, such as regulating osmotic pressure within the internal environment and maintaining acid-base balance. However, the interaction between amino acids and protein function remains poorly understood. How to minimize interference from complex cellular factors and better elucidate the interactions between amino acid molecules and proteins has become one of the key challenges in international proteomics research.
Peptides play a crucial role in the growth, development, and metabolism of organisms. They consist of amino acids linked by peptide bonds in a specific sequence. Two amino acids form a dipeptide, three form a tripeptide, and so on. Typically, peptides with fewer than 10 amino acids are referred to as small molecular peptides or oligopeptides, whereas those with more than 10 are termed polypeptides. Amino acids contain both amino and carboxyl groups, which exist as zwitterions under neutral conditions and cannot directly converge to synthesize peptides. Therefore, synthesizing peptides with a defined sequence requires not only activating the carboxyl group but also protecting non-reactive N-terminal amino groups and active side chains.
Peptide synthesis relies heavily on protected amino acids, and the efficiency and yield of peptide synthesis are significantly influenced by the choice of protective groups. Based on the reactivity of side chains during peptide synthesis, the 20 natural amino acids can be classified into inert side chain amino acids (e.g., Gly, Leu, Ile, Ala, Val, Phe, etc.) and active side chain amino acids (e.g., side chain carboxyl, side chain amino, side chain thiol, and side chain heterocyclic groups). The former type requires only protection of the α-amino group, whereas the latter necessitates additional protection of the reactive side chain groups. Since the main chain protection group is removed during peptide attachment and the side chain protection group is removed afterward, the two protection groups must have distinct removal conditions.
Different amino acids require appropriate protective groups tailored to their characteristics, and the selection of protective groups varies depending on the type of synthetic peptide. First, it is essential to ensure selective protection of the groups requiring protection under conditions that maximize reaction yield while ensuring the stability of the protected amino acids. Second, the protective group must be selectively removed in high yield after peptide synthesis without affecting the resulting peptide bond. Protective groups that can be removed under mild conditions are currently developing at a rapid pace.
Tert-butoxycarbonyl (Boc) is a critically important amino protection group that exhibits sensitivity to acid hydrolysis yet maintains a certain degree of stability, being stable to alkali and catalytic hydrogen hydrolysis. Most amino acids can be crystallized when protected with Boc, making it widely used in amino acid preservation.